什么是工程热塑性?Such a definition is difficult to arrive at and is very subjective, but, for the purposes of this review article, any thermoplastic that can be formed into a load-bearing shape that might otherwise be formed from, for example, steel or wood will be classed as an engineering thermoplastic.这篇综述仅限于未加固和短纤维增强的热塑性塑料,其中增强纤维(通常是玻璃或碳)的长度通常小于2-3 mm。 热塑性塑料比传统材料具有许多优势,包括:低密度;欧洲杯足球竞彩制造能源低;处理成本低;以及相对容易制作复杂形状的能力。 热塑性特性Thermoplastic materials generally fall within two classes of molecular arrangement, amorphous and semi-crystalline (see figure 1).
|
Figure1.聚合物链的分子排列 |
表1列出了无定形和半晶聚合物的选择。 表格1。无定形和半晶聚合物。
Amorphous |
Polyamideimide |
聚醚醚酮 |
Polyethersulphone |
Polytetrafluoroethylene |
Polyetherimide |
Polyamide 6,6 |
多核心 |
聚酰胺11 |
多硫磺 |
聚苯基硫化物 |
Polyamide (amorphous) |
聚对苯二甲酸 |
Polymethylmethacrylate |
Polyoxymethylene |
聚氯乙烯 |
Polypropylene |
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene |
High Density Polyethylene |
Polystyrene |
Low Density Polyethylene |
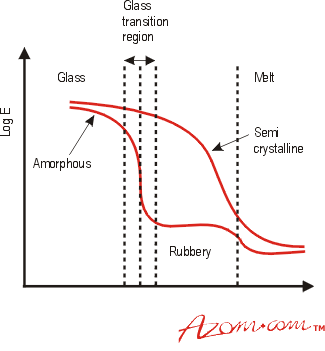
无定形聚合物通常,完全无形的聚合物在处女状态下僵硬,脆弱和透明。温度和应力状态对分子排列具有深远的影响,因此是聚合物的特性。Under the action of sufficient stress, the polymer chains can uncoil and align over a period of time.在升高的温度下,聚合物链具有足够的能量,可以进一步旋转和盘绕。 图2从示意性地显示了温度对无定形和半晶聚合物弹性模量的影响。Below a temperature known as the glass transition temperature, Tg, the structure of amorphous polymers is termed 'glassy', with a random arrangement of the polymer chains, similar to the random molecular arrangement found in glass.随着温度升高到TG,聚合物链具有足够的热能旋转,导致模量下降。One definition of Tg is the temperature at which molecular rotation about single bonds becomes favourable as the temperature increases.在TG以上但低于熔化温度的温度下,TM有一个“橡胶区域”,该材料在相对较低的负载下显示出较大的伸长率。通常在其TG以下的温度下使用非晶的热塑性塑料,就像玻璃一样脆弱。There are, however, certain exceptions.聚碳酸酯(PC)是无定形的,但在远低于其TG的温度下被认为很难。When it does fracture below its Tg, it does so in a brittle manner, but this requires a large amount of energy and so PC is considered tough, finding use in applications requiring impact resistance, e.g. safety helmets and bullet proof glazing.This behaviour is due to the chemical bonds in polycarbonate rather than the arrangement of the polymer chains.
|
Figure 2.The effect of temperature on the Elastic Modulus (assuming both types of polymer have the same Tg and Tm) |
Semi-Crystalline Polymers半晶材料(例如聚酰胺)没有表现出透欧洲杯足球竞彩明的TG或“橡胶”区域,尽管通常会引用一种结构的无定形部分会进行某种过渡。对于这些聚合物,当晶体区域分解时,主要过渡发生在TM处(见图2)。Some chain rotation in the amorphous regions will occur below Tm, giving some impact resistance at these temperatures.表2给出了许多聚合物的TG和TM值。 表2。Glass transition and melting temperatures for a range of thermoplastics.
聚合物 |
TM(°C) |
高密度聚乙烯(HDPE) |
- |
135 |
聚丙烯(PP) |
-10 |
175 |
Polystyrene (PS) |
100 |
- |
聚甲基丙烯酸酯(PMMA) |
105 |
- |
聚氯乙烯(PVC) |
65 |
- |
天然橡胶(NR) |
-75 |
25 |
Polydimethyl siloxane (PDMS) |
-125 |
-55 |
Polyoxymethylene (POM) |
-30 |
175 |
聚碳酸酯(PC) |
150 |
- |
聚对苯二甲酸(PET) |
70 |
265 |
聚醚醚酮(PEEK) |
145 |
335 |
尼龙6(PA6) |
50 |
215 |
Polyamideimide (PAI) |
295 |
- |
polysulphone(psul) |
195 |
- |
聚苯基硫化物(PPS) |
90 |
285 |
聚乙烯氨(PES) |
230 |
- |
聚醚酰亚胺(PEI) |
218 |
- |
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
20 |
325 |
Liquid crystal polymer (LCP) |
- |
420 |
表2。Values of Tg and Tm for selected polymers |