2017年7月26日
研究人员已经开发Kyoto University’s Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) and the University of Tokyo.
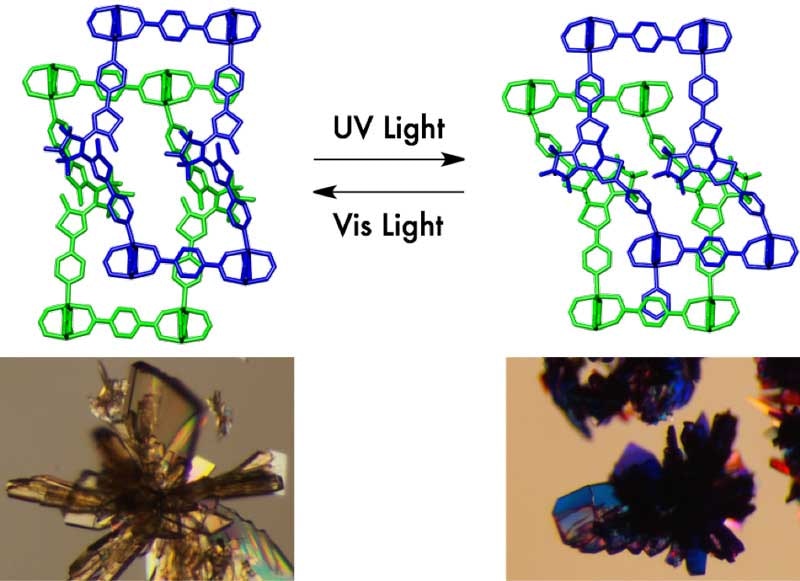 Entangled porous coordination polymers like ‘wire-and string puzzles’ enable reversible and repeatable photomodulation of CO2 sorption. The single crystals of the porous material showed a drastic color change upon irradiation of ultraviolet and visible light. Credit: KYOTO UNIVERSITY ICEMS
Entangled porous coordination polymers like ‘wire-and string puzzles’ enable reversible and repeatable photomodulation of CO2 sorption. The single crystals of the porous material showed a drastic color change upon irradiation of ultraviolet and visible light. Credit: KYOTO UNIVERSITY ICEMS
当暴露于光线时,光致变色分子会改变其化学结构或电子状态。这些分子在能够用于控制药物释放或生产用于组织工程的动态支架的“光响应”材料的开发中起着至关重要的作用。欧洲杯足球竞彩但是,迄今为止,由于材料太坚固而无法允许可逆和可重复的更改,因此已经确定了它们欧洲杯足球竞彩与固体材料的使用。
ICEMS的Susumu Kitagawa,东京大学的Hiroshi Sato及其同事开发了一种柔性的多孔晶体,由光反应性二乙烯基乙烯衍生物组成,锌离子(Zn)(Zn)2+)和1,4-苯并二羧酸盐。
The ‘porous coordination polymer’ comprised of two-dimensional sheets attached by pillars of photoresponsive molecules, which developed a three-dimensional, entangled framework. The entwined components are compared to twisted metal wire and string puzzles by the Researchers.
The channels changed shape when exposed to light because of the flexible nature of the entangled framework. When exposed to ultraviolet irradiation, the distance between the two layers shrank and when lit by visible light it expanded.
材料对摄取二氧化碳的潜力(CO2)was tested by the Researchers. The material adsorbed up to 136 ml of CO2当它不被照射时。当暴露于紫外线时,毛孔缩小了,还原Co2吸附至108 mL。co2暴露于可见光时,吸收再次增加到129 mL。重新暴露于紫外线导致降低至96毫升。
聚合物的纠缠框架允许这些可重复和可逆的CO2absorption changes; it makes room for the photoresponsive molecules to change while permitting them to discharge their strain into the flexible material.
初始测试指定的是,多孔晶体还能够在不同温度下吸附其他气体,例如氮气,但是需要深入分析。
“Our strategy will grant access to a new dimension of porous compounds as platforms for various photochemical conversions and the photomodulation of porous properties,”conclude the Researchers in their study, featured in the journal Nature Communications.