Aug 6 2019
An innovative system designed by engineers can help cool buildings in packed metropolitan areas without using any electricity—a major breakthrough at a time when cities are trying to adjust to climate change.
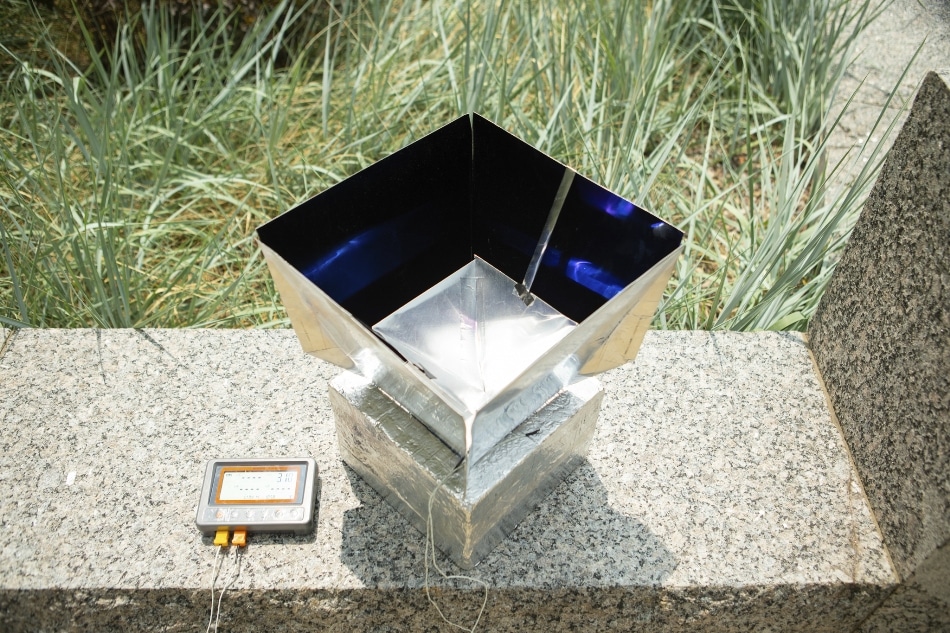 The system helps cool its surroundings by absorbing heat from the air inside the box and transmitting that energy through the Earth’s atmosphere into outer space. (Credit: University at Buffalo.
The system helps cool its surroundings by absorbing heat from the air inside the box and transmitting that energy through the Earth’s atmosphere into outer space. (Credit: University at Buffalo.
The new system includes an unusual material—a low-cost polymer/aluminum film —that is fitted within a box at the base of an exclusively developed solar “shelter.” This polymer/aluminum film absorbs heat from the air present inside the box and transmits that energy via the Earth’s atmosphere into the outer space. This process helps in keeping the surroundings cool.
太阳能“庇护所”具有双重目的 - 它阻止了传入的阳光,并同时横向射击从膜向天空产生的热辐射。
The polymer stays cool as it dissipates heat through thermal radiation, and can then cool down the environment. This is called radiative or passive cooling, and it’s very interesting because it does not consume electricity—it won’t need a battery or other electricity source to realize cooling。
Lyu Zhou, Study Co-First Author and PhD Candidate, Electrical Engineering, School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, University at Buffalo
“One of the innovations of our system is the ability to purposefully direct thermal emissions toward the sky”首席研究员Qiaoqiang Gan博士兼电气工程副教授University at Buffalo((UB). “通常,热排放朝各个方向传播。我们找到了一种沿狭窄方向射击的方法。
甘继续说:“this enables the system to be more effective in urban environments, where there are tall buildings on all sides. We use low-cost, commercially available materials, and find that they perform very well。”
总体而言,由工程师设计的庇护箱系统的尺寸约为10英寸,高18英寸(45.72厘米)和10英寸长(25.4厘米)。要冷却单个建筑物,需要安装系统的许多单元才能覆盖屋顶。
该研究的结果已发表在自然的可持续性on August 5th, 2019. The research was an international association between Gan’s team at UB, Zongfu Yu’s team at the University of Wisconsin–Madison; and Boon Ooi’s team at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) in Saudi Arabia.
In addition to Zhou, Haomin Song, PhD, UB assistant professor of research in electrical engineering, and Jianwei Liang at KAUST are co-first authors of the study. The National Science Foundation partly funded the study.
A System that Works During the Day and in Crowded Environments
创新的被动冷却系统解决了该领域的一个主要问题 - 辐射冷却如何在包装的城市地区和白天运行?
在夜间,辐射冷却很容易,因为我们没有太阳能输入,因此热排放刚出去,我们很容易意识到辐射冷却。但是白天冷却是一个挑战,因为阳光明媚。在这种情况下,您需要找到防止屋顶加热的策略。您还需要找到不吸收太阳能的发射材料。欧洲杯足球竞彩我们的系统应对这些挑战。
Haomin Song, PhD, Assistant Professor of Research, Electrical Engineering, University at Buffalo
当热量膜和太阳能避难所在白天放置在外面时,它有助于降低紧凑,封闭空间的温度高达6°C(11°F)。在夜晚,该数字增加到大约11°C(约20°F)。
创新的架构如何驱动辐射冷却
最新的辐射冷却系统集成了几种具有光学迷人的设计功能。聚合物/金属膜是核心成分之一,是用涂有透明聚合物聚合物聚合物聚合物聚合物的铝板制成的。虽然铝会反射出铝,但周围空气中的热量被聚合物吸收并消散。
该材料放在泡沫盒的底部,并在盒子上建造了太阳能“庇护所”。这是通过利用太阳能吸收材料来建造四个向外倾斜的墙壁以及这些墙内倒置的正方形锥体来完成的。
该设计具有双重目的 - 首先,它有助于吸收阳光,其次,锥形和墙壁的形状将膜产生的热量引导到天空中。
“如果您查看汽车的大灯,它具有一定的结构,使其可以将光线引导到一定方向,”甘说。“We follow this kind of a design. The structure of our beam-shaping system increases our access to the sky. The ability to direct the emissions improves the performance of the system in crowded areas。”
Source:http://www.buffalo.edu/