期刊上提出的一项新研究Coatings已经研究了影响细菌粘附于假体和矫形材料以及缓解溶液的因素。欧洲杯足球竞彩

Bacterial Adhesion on Prosthetic and Orthotic Material Surfaces。图片来源:Seventyfour/Shutterstock.com
最近的市场研究表明,全世界的假体和矫形器的使用都在增加,这主要是由于儿童和老年人的糖尿病患病率不断增长。
这些移动性辅助设备旨在人为地替换损失的肢体或身体部位,或者提供额外的支持以使运动更容易。
Because these devices are directly in contact with the user’s skin for long periods of time – particularly the inner sides of prosthetic sockets and orthotic devices – there is a clear need to help manage the levels of the potential foreign microorganisms present and limit any risk of infection to the user from harmful bacteria, fungi or viruses.
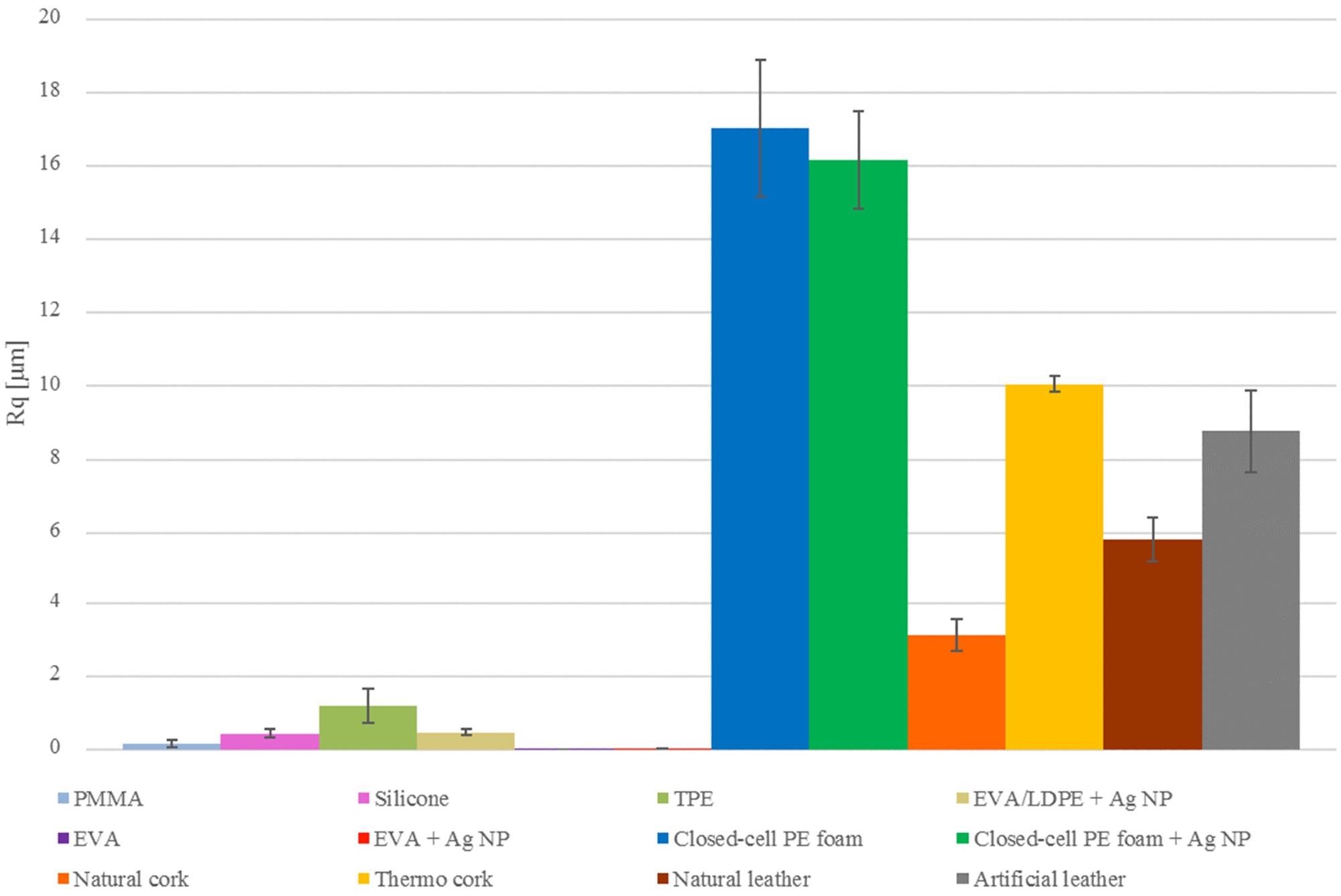
RMS roughness Rq用轮廓仪测量的矫形和假肢表面。图片来源:Abram,A等人,涂料
Bacteria such as staphylococcus (S.) aureus and S. epidermidis are almost constantly resident on a person’s skin, and there is a risk that some strains of these bacteria may adhere to prostheses and orthoses’ solid surfaces and develop biofilms which may, in turn, lead to infections when these are in contact with an impaired skin barrier.
This phenomenon of bacteria becoming firmly attached to surfaces is typically referred to as bacterial adhesion.
正在进行研究可能影响细菌粘附的因素,但已经发现这些因素包括表面电荷,表面疏水性和材料的表面粗糙度。
A number of historic studies into bacterial adhesion to medical devices have looked into the adhesion of staphylococci bacteria to the materials used for implantable medical devices, but the paper’s authors report that they did not find any studies exploring the adhesion of bacteria to prosthetic and orthotic materials.
考虑到这一点,他们旨在证明通常与皮肤接触的不同假肢和矫形材料的表面特性如何影响粘附在材料表面上的金黄色葡萄球菌和表皮链球菌的能力和可能性。欧洲杯足球竞彩
作者评估了最常用的矫形器和假肢设备材料,研究了材料吸引通常存在于皮肤上的细菌的能力。欧洲杯足球竞彩
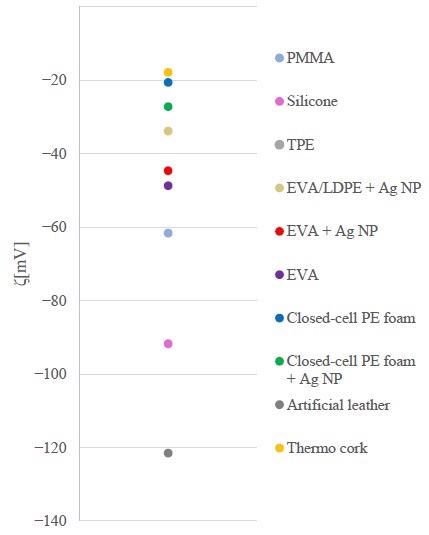
矫形和假肢材料表面的Zeta电位。图片来源:Abram,A等人,涂料
This particular study was focused on the materials’ surface characteristics such as wetting, surface charge, roughness, and morphology.
Twelve different materials typically used in prosthetics and orthotics were evaluated, including two natural materials (natural leather and natural cork) and ten synthetic materials including ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), silicone, artificial leather, and poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA).
In order to look at a possible means of better mitigating this bacterial adhesion, the authors also evaluated the potential of silver nanoparticle coatings to affect the bacterial adhesion to materials – a novel approach, since almost all studies of S. aureus and S. epidermidis’ adhesion to material surfaces have historically focused on the titanium and titanium alloys employed in implants. To this end, three of the materials investigated included these coatings.
Bacteria with hydrophobic properties have been found to attach more robustly to the surfaces of similarly hydrophobic materials – more so than the adhesion of hydrophilic bacteria. Hydrophobic materials have been noted to be less resistant to bacterial adhesion than hydrophilic materials.
表面粗糙度(例如,诸如酒窝,凹槽和裂纹)的缺陷也被发现鼓励细菌粘附和生物膜的发展。
Another factor that can impact the potential for bacterial adhesion is a surface charge. The majority of solid surfaces and bacteria are negatively charged and should bacteria and a material’s surface exhibit the same charge, repulsive electrostatic forces will cause an energy barrier that prevents adhesion.
SEM显微照片用于评估细菌粘附的程度,而数据是在一系列材料的表面地形,粗糙度,疏水性和ZETA电位上获取的。欧洲杯足球竞彩
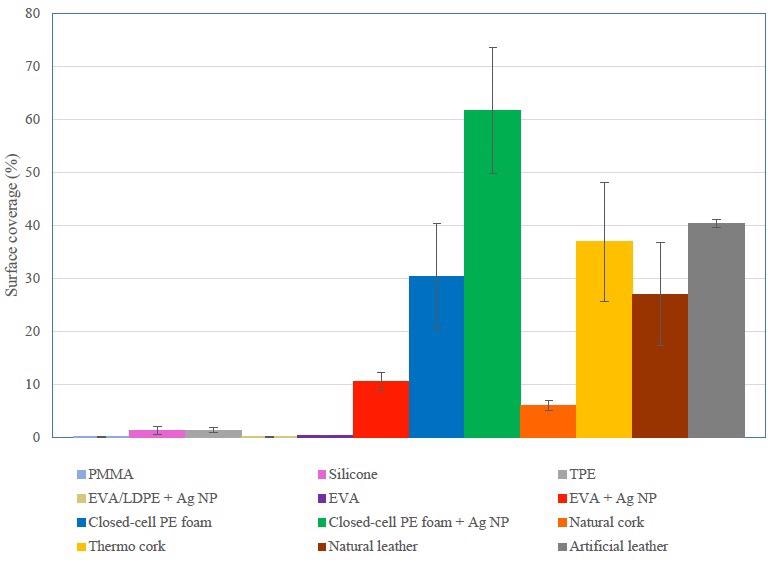
基于SEM显微照片的评估,不同矫形器和假肢材料的表面覆盖范围。欧洲杯足球竞彩在前四个表面上,表皮链球菌被粘附,而在其余的表面上,金黄色葡萄球菌粘附。图片来源:Abram,A等人,涂料
这项研究表明,在分析的人造皮革和热软木塞上存在最突出的细菌粘附,而在乙烯乙酸乙烯酯样品上观察到了最不突出的细菌粘附。作者得出的结论是,这种材料的特定表面特征(例如粗糙度,疏水性和电荷)是这种降低的细菌粘附的关键因素。
通过更好地了解哪种矫形和假肢材料能够减少在皮肤上发现的细菌时减少细菌粘附,这些重要装置的制造商将能够选择专门欧洲杯足球竞彩减少它的材料。
This will ultimately reduce the risk of bacterial infection and help to protect users of prosthetics and orthotics more effectively.
参考
艾布拉姆(Abram),阿Že,阿纳玛利亚·佐尔(Anamarija Zore),UrbanLipovž,AnitaKošak,Maja Gavras,ŽanBoltežar和Klemen Bohinc。2021年。“对假体和矫形物材料表面的细菌粘附”Coatings11,不。12:1469。https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6412/11/12/1469
Cision。2021年。“全球价值131.2亿美元的假肢市场,到2028年为4.51%https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/prosthetics-market-worth-worth--13-12-12-12-blobally-by-2028-AT-4-51--cagr-cagr-cagr-verified-market-Market-Market-Market-MarkEarch-301287440。html
Disclaimer: The views expressed here are those of the author expressed in their private capacity and do not necessarily represent the views of AZoM.com Limited T/A AZoNetwork the owner and operator of this website. This disclaimer forms part of theTerms and conditionsof use of this website.