写入可持续性一支来自中国的科学家团队报告了一种使用AC激励方法的快速充电策略,这些方法可改善当前充电策略。
Study:A Novel DC-AC Fast Charging Technology for Lithium-Ion Power Battery at Low-Temperatures。Image Credit: GzP_Design/Shutterstock.com
锂离子电池
As society rapidly decarbonizes and electrifies, there is a pressing need for reliable energy storage devices that can meet the rigors of current technological demands and mitigate the problems caused by climate change. Li-ion batteries are used in a multitude of electronic devices. They are a central technology in electric vehicles due to their enhanced energy density, reliability, and durability.
但是,有一些带有锂离子电池的缺点,尤其是在低温条件下。这些设备可能会遭受电解质的离子电导率弱,SEI膜的弱电导率和较低的化学反应速率。此外,由于用作阳极的石墨颗粒中离子的扩散系数较低,它们可能会经历缓慢的充电。欧洲杯猜球平台
在较低温度下的另一个关键问题是电荷循环中锂离子的积累以及电池负面表面上的锂金属的形成。长期树突增长会导致严重的装置损坏,从而影响电池的寿命并引起潜在的安全问题。
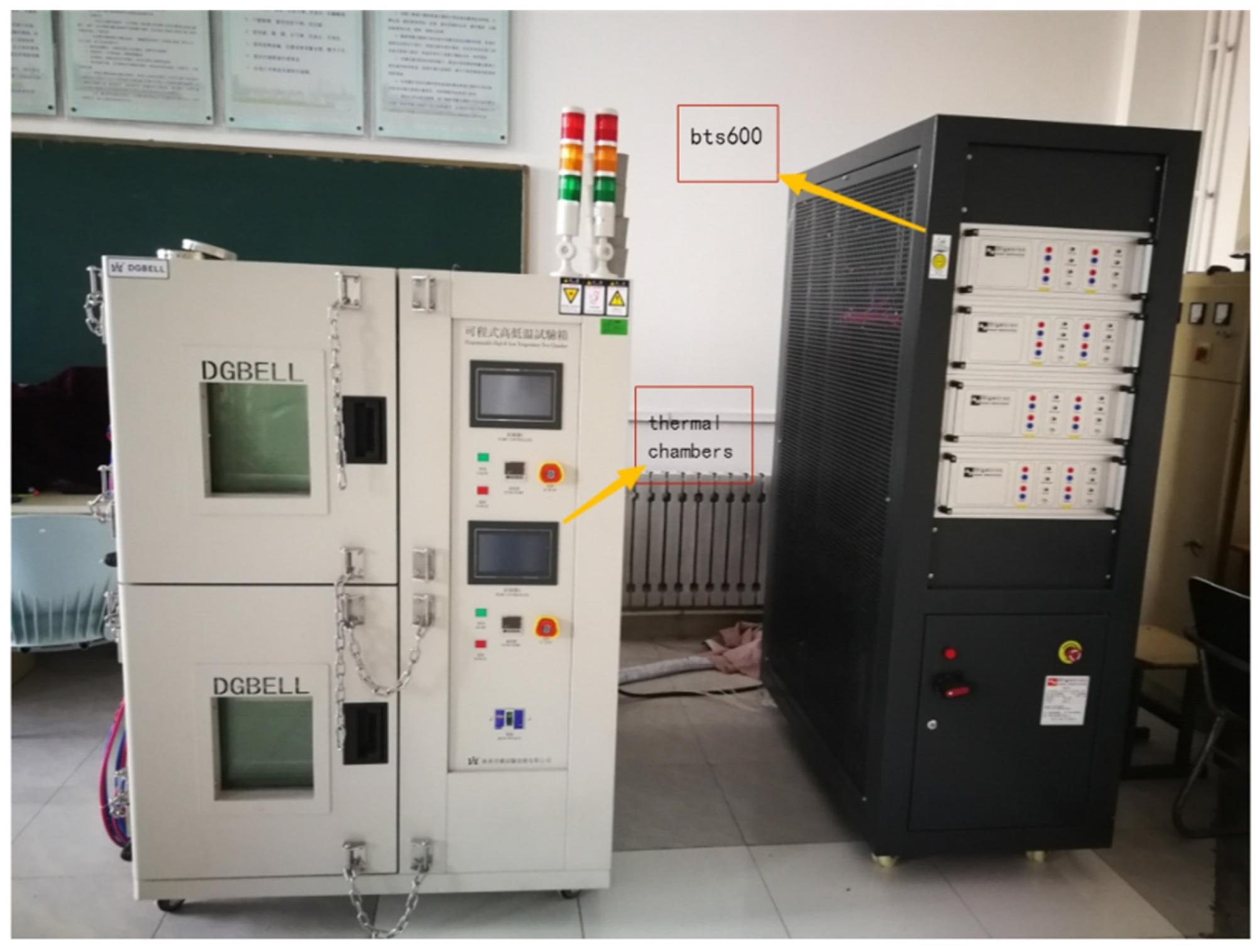

The BTS600 and thermal chamber. Image Credit: Guo, S. et al., Sustainability
低温电池充电的当前策略
There is a need for a dependable low-temperature rapid charging strategy to improve the efficiency, durability, and reliability of Li-ion batteries. Researchers have developed several strategies in recent years which use internal and external heating.
外部加热策略包括使用液体和温暖空气等方法提供必要的温度。但是,这些方法遇到了几个缺点。温度分布不均匀,加热速率和低效率都阻碍了外部加热方法的广泛使用。
Due to the challenges associated with these methods, there has been growing research interest in methods that use internal heating to achieve fast and reliable low-temperature charging. Common strategies include pulse heating, self-heating methods, and convection heating.
交流逆变器。图片来源:Guo,S。等,可持续性
The Study
The paper has proposed a novel strategy for fast, low-temperature charging of Li-ion batteries. The method overcomes negative effects which otherwise limit the efficiency and reliability of batteries when charged under these conditions.
该策略通过在过程中实现足够的温度升高来帮助满足电池充电的需求。作者通过研究充电率和频率选择来获得最佳参数。此外,与当前使用的CCCV方法相比,拟议方法的损失和充电效率的损失是定量的。
In the research, a thermal chamber was selected to provide the external temperature conditions. The battery’s capacity was calibrated by a BTS 600 machine. An inverter provided the AC power for charging, with the battery charge and discharge process controlled by a computer, which also recorded the data for analysis. Temperature, voltage, and current sensors provided real-time monitoring and information.
外部环境温度为0oC和5o在测试室中使用C评估温度效应,电池持续了2小时,以确保电池的温度达到环境温度。然后在不同的SOC和温度下评估CCCV和Ac-Incentive充电策略。
使用CCCV充电将电池充电到指定的SOC点,随后使用测试室进行温度调节。2小时后,达到所需的电池温度。然后使用这两种策略将电池充电到所需的电压。在实验过程中,测量了温度,电流和电压。
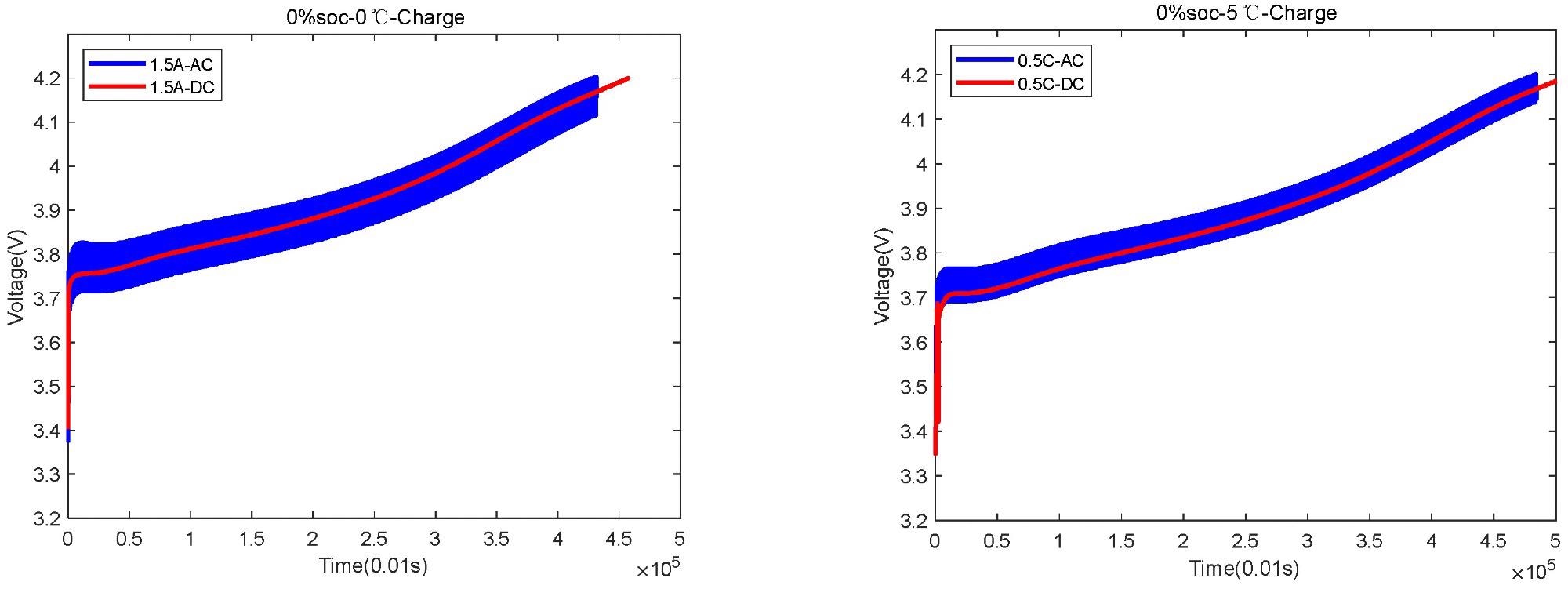
The voltage changes in the case of charging starting at 0% SOC at 0 °C and 5 °C, respectively. Image Credit: Guo, S. et al., Sustainability
研究结果
实验观察结果证实了一种对低温快速充电的官能策略的适用性。Ac-Incentive策略符合所需的费用值比CCCV方法快20%。此外,作者观察到了接种策略的波动升高,导致温度升高。
The average temperature rise in the AC-incentive strategy was 2-4oC compared to the CCCV strategy. Therefore, the authors concluded that the AC strategy significantly reduces the time needed to charge Li-ion batteries in low-temperature conditions. At all temperatures and SOC conditions evaluated in the research, the charge time was significantly reduced using the AC strategy.
综上所述
该论文证明了使用接头策略快速低温锂离子充电的优势。在所有测试条件下,AC策略比CCCV充电策略更有效。
作者指出,未来的工作将涉及评估拟议策略在低温条件下使用电动汽车的实际应用。
Further Reading
Guo,S。等。(2022)一种新型的DC-AC在低温下用于锂离子电池的快速充电技术可持续性14((11)6544[online] mdpi.com. Available at:https://www.mdpi.com/2071-1050/14/11/6544
免责声明:此处表达的观点是以其私人身份表达的作者的观点,不一定代表AZOM.com的观点有限的T/A Azonetwork本网站的所有者和运营商。此免责声明构成了条款和条件使用此网站。